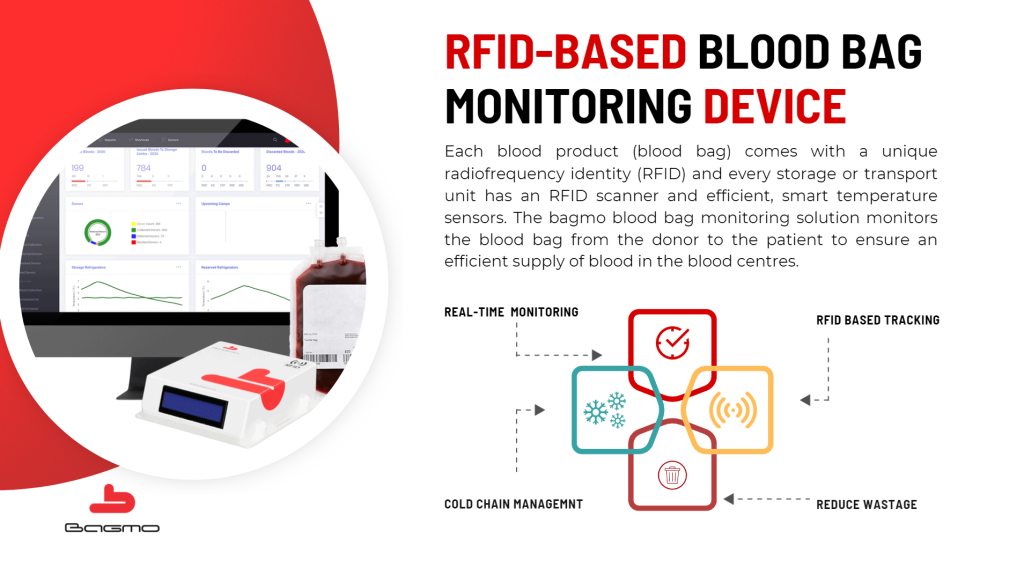
Managing a blood center is crucial because it involves collecting, storing, and delivering blood to patients. One helpful technology for this is RFID (Radio-Frequency Identification). RFID allows blood banks to keep track of blood bags in real time, monitor their temperature, and maintain a detailed record of where the blood has been from the time it was donated to when it’s given to a patient. Utilizing RFID blood bank software for centralized, comprehensive inventory management.
RFID works by using radio waves to identify and track objects. Each blood bag gets a special RFID tag with a unique code. RFID readers at the blood centre, during transport, and at hospitals can pick up these tags and give real-time info about where the blood is, what condition it’s in, and where it has been.
This kind of tracking helps make sure that the blood stays safe and can be used when needed. It’s a big deal for making blood banking more efficient and cost-effective.
RFID (Radio-Frequency Identification) technology is revolutionizing the way blood centre manage their operations by enabling complete end-to-end (vein-to-vein) monitoring. This system provides a fully traceable, real-time solution that tracks blood from the moment it is donated to the point of transfusion, ensuring quality and safety at every stage.
Vein-to-vein monitoring means every blood bag is assigned a unique RFID tag, and its movement, storage, temperature conditions, and overall handling are continuously monitored. This technology provides comprehensive tracking throughout the blood’s entire journey, ensuring that blood banks maintain regulatory compliance and issue safe, quality-assured blood to patients.
Advantages of RFID-based complete end-to-end (vein-to-vein) monitoring.
1. Real-Time Tracking of Blood Bags
RFID tags are attached to each blood bag, containing a unique identifier. These tags communicate with RFID readers placed at various key points—such as storage areas, transport vehicles, and hospitals. The system provides real-time visibility into the location and movement of each blood bag, ensuring complete vein-to-vein traceability from donation to transfusion.
This real-time tracking ensures that blood is handled and stored properly at all times, reducing the risk of lost or mishandled blood bags and providing critical information at every stage of the process.
2. Automated Inventory Management
One of the most significant benefits of RFID in blood banks is automated inventory management. When a blood bag is scanned, all its details — such as blood type, expiry date, and donor information—are automatically updated in the system.
This system helps prevent mistakes and makes sure that the correct blood type is always on hand and can be easily located. It also helps blood banks keep track of their supplies so that hospitals can get the blood they need quickly.
3. Temperature Monitoring and Alerts
Blood must be stored at precise temperatures to remain safe and effective. RFID tags with built-in temperature sensors are attached to blood bags or storage containers, continuously monitoring the temperature in real time.
If the temperature of a blood bag goes outside of the safe range while it’s being stored or moved, the system can send out alerts right away through text, email, phone calls, or WhatsApp. This helps make sure that the blood stays safe to use. It’s an important way to follow safety rules and make sure patients only get good blood products.
4. Streamlined Blood Bag Identification
Blood banks usually use manual barcode scanning to keep track of blood bags, which can be quite time-consuming. RFID technology makes this process much faster and easier. With RFID, staff can simply wave the blood bags near RFID readers, and all the important information is instantly captured by the system. This makes things run more smoothly, especially for blood centres that handle a lot of blood bags, as it cuts down on the time needed to find the right bag and makes the whole process more efficient.
5. Improved Data Accuracy and Security
RFID technology enhances the accuracy of data recorded in blood bank software, minimizing the risk of incorrect data entry. Because RFID automatically tracks the movement and status of blood bags, the system reduces human error and ensures accurate, real-time data.
Additionally, RFID improves security by keeping a detailed log of each blood bag’s movement and the environmental conditions it’s exposed to, ensuring a secure and traceable process from donation to transfusion.
6. Regulatory Compliance
RFID technology helps blood banks keep blood safe by constantly checking the temperature and other conditions. This makes sure that all the rules about safety are being followed and lets the blood banks keep really good records. This kind of transparency is important for making sure the blood is always the best quality and very safe to use.
How RFID Enables End-to-End Monitoring
RFID tags, which are placed on each blood bag, communicate with RFID readers in storage facilities, transport vehicles, and hospitals. These tags capture critical data, such as the blood bag’s location and temperature. The system automatically updates blood bank software in real time, offering complete visibility into the entire lifecycle of each blood donation.
What do we need to ensure before implementing an RFID-based blood bank management system?
Important Considerations for Successful RFID Implementation in Blood Banks To make sure that RFID technology works well in blood bank management applications, there are several important things to keep in mind for a smooth, efficient, and cost-effective integration:
1. Easy Installation
The RFID system should be easy to install without the need for major changes to existing equipment. This means that blood centres can adopt RFID technology without having to replace their current refrigerators and cold rooms, which helps to save money and prevent disruptions to their operations.
2. Affordable Tracking
The RFID tags used for tracking should be affordable, ideally costing between ₹10 to ₹30 per tag. This helps blood centres, especially those with limited resources, to track each blood bag without spending too much money.
3. Reusable Tags
Using reusable RFID tags can help to cut down on recurring costs for blood banks.
4. No Impact on Storage Space
When implementing RFID technology, it’s important to ensure that it doesn’t take up extra space in refrigerators or cold rooms. The RFID tags, sensors, and readers should be designed to fit within the existing space so that blood banks can maintain their storage capacity.
5. Seamless Integration with blood bank software
The RFID system should be fully integrated with the blood bank’s information system, allowing for easy management of inventory and tracking. The blood centre management application should also be customizable to fit the specific needs of each blood center, making it easier to use and reducing the risk of errors.
Why Assuring These Factors is Essential
Ensuring these factors are in place guarantees that the RFID-based vein-to-vein monitoring system is cost-effective, efficient, and adaptable. By implementing a solution that integrates seamlessly into existing infrastructure and fits within budgetary constraints, blood banks can enhance their operations without facing major disruptions or increased operational costs.
- Retrofittable RFID systems allow for a seamless transition to advanced technology without requiring expensive infrastructure changes.
- Cost-effective and reusable tags help blood banks manage their operations within budget, while ensuring sustainability.
- No impact on storage capacity means that blood banks can maintain efficiency in their inventory management.
- Customizable software integration ensures that blood banks have a system that meets their specific needs, improving operational efficiency and patient safety.
Conclusion
An RFID-based vein-to-vein monitoring system provides complete visibility into every blood bag’s journey, from donation to transfusion. For successful implementation, blood banks must ensure that the system is retrofittable, cost-effective, reusable, non-disruptive to storage, and fully integrated with customizable blood bank software. When these factors are assured, blood centres can offer quality-assured blood to patients while maximizing efficiency, minimizing costs, and ensuring safety at every stage.